CIRCULATORY SYSTEM ANATOMY
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM ANATOMY
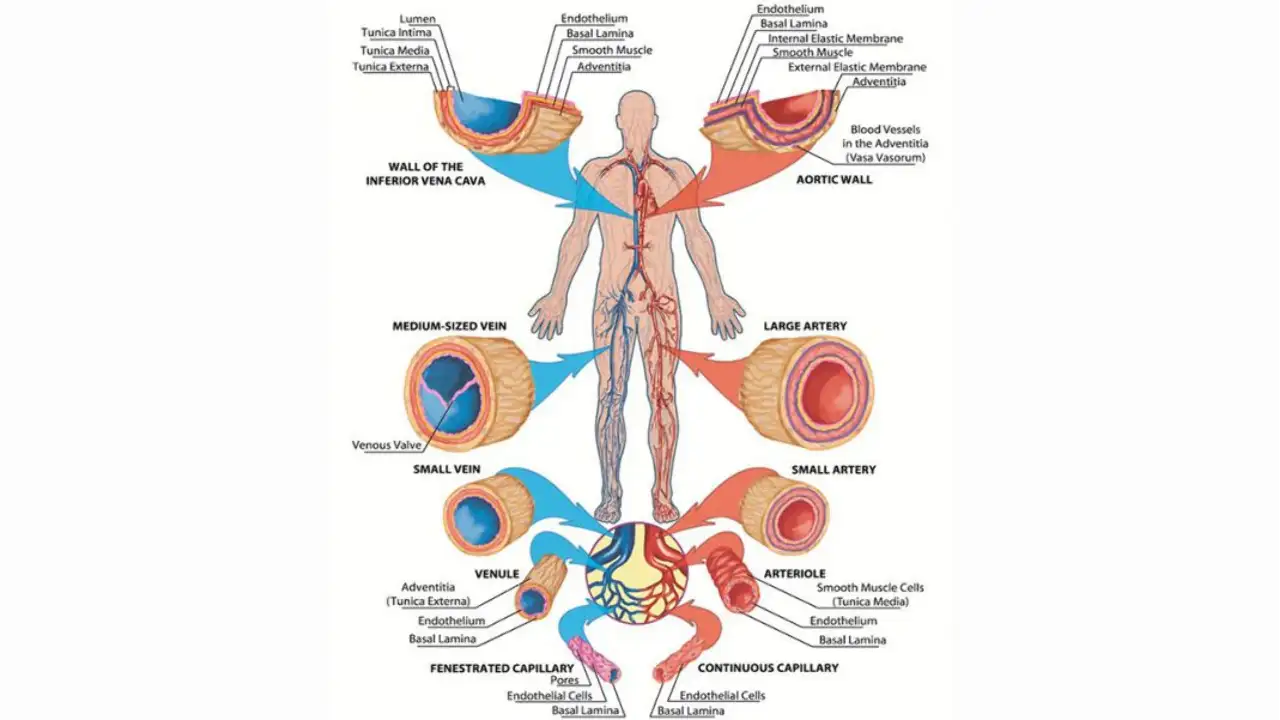
It comprises
- A central pump (the Heart)
- A set of out-going blood vessels (Arteries);
- A set of in-coming blood-vessels (Veins);
- An over-flow system (Capillaries, Lymphatic).
We have finished with the last three; now we take up the Heart and Blood.
The Heart is a muscular body comprising
- Sides
- Right—containing
- An Auricle
- A Ventricle
- An Auriculo-Ventricular Septum
- Left-containing
- An Auricle
- A Ventricle
- An Auriculo-Ventricular Septum
- Right—containing
Into the heart pours—
- Impure blood,
- Superior Vena Cava
- Inferior Vena Cave
- Food-laden material (chyle)
- in Thoracic Duct via,
- Left Innominate
- Lymph from all parts
- Purified blood—via, Pulmonary vein.
- From the heart goes out-
- Impure blood-into lungs via, Pulmonary Artery.
- Purified blood-into whole body via,
The impure blood from lower parts of the body is collected into the inferior vena cava, that passes through the liver and opens into the Right Auricle or Atrium of heart. Similarly, impure blood of all upper parts of the body is collected into the superior vena cava, which also discharges itself into the right auricle or Atrium of the heart. As soon as the right auricle gets filled with blood it contracts and thereby forces the blood into the right ventricle-the Right auriculo-ventricular (also called Tricuspid Valve) preventing the flow of blood backward from right ventricle into auricle. As soon as the right ventricle gets filled, it sends the blood via the pulmonary artery into the lungs to be oxygenated there. After being oxygenated, the blood from the right and left lungs is propelled via the pulmonary veins into left auricle or atrium. From this left auricle, past the Left Auriculo Ventricular Valve (also called Mitral Bicuspid Valve), blood is forced into the left ventricle. When this left ventricle contracts, blood is forced into the Aorta (the main arterial trunk of the body) and thence to all parts of the body.
The heart is an irregular flattened cone in shape with its base upwards. It lies opposite the 5th, 6th, 7th and 8th dorsal spinal bones. Its apex (formed chiefly by the left ventricle) lies 3½ inches from middle line of body, opposite the 5th left inter-costal space. It is enclosed inside a firm fibrous bag, called pericardium and its interior is lined by a delicate membrane called endocardium. Its blood-supply is by means of coronary arteries, which can, act during the period of rest of heart, called diastole.
Blood-is a thick fluid, composed of two parts
- Liquid—Serum or Plasma
- Solid—Corpuscles
- White (leucocytes)
- Red (erythrocytes)
It is the preponderance of red blood corpuscles with their coloring matter, called hemoglobin that gives to blood the red colour that it has got. Blood has the property of clotting or coagulating, when shed.
Comments are closed.